Cork powder and granules – ecological applications

Cork powder and granules are the main by-products of the cork industry, one of the leading economic activities in Portugal and other Mediterranean countries. Cork powder and granules – ecological applications for this product are anticipated, ranging from cork stoppers to agglomerates and briquettes for use as an adsorbent in the treatment of gaseous emissions, water and wastewater.
Cork powder and granules – ecological applications – cork biomass was used in its original form as a biosorbent for heavy metals and oils, and is also an activated carbon precursor for removing organic pollutants in water and volatile organic compounds in the gas phase.
The use of cork to solve environmental problems, namely oil spills, is the first commercial application of the cork potential of sorbent. The variety of raw materials that can be produced or extracted from cork has attracted the attention of many researchers.

The chemical composition of cork has been studied since the 18th century (Conde et al., 1998), but full knowledge of the chemical properties of cork, and even less of all its potential uses and transformations, is not yet complete.
In addition, since the beginning of the 21st century, the Portuguese cork industry has been investing in research and development: in the period 2000-2002 alone, 35 patents were registered, while in the previous decade only 19 were registered.
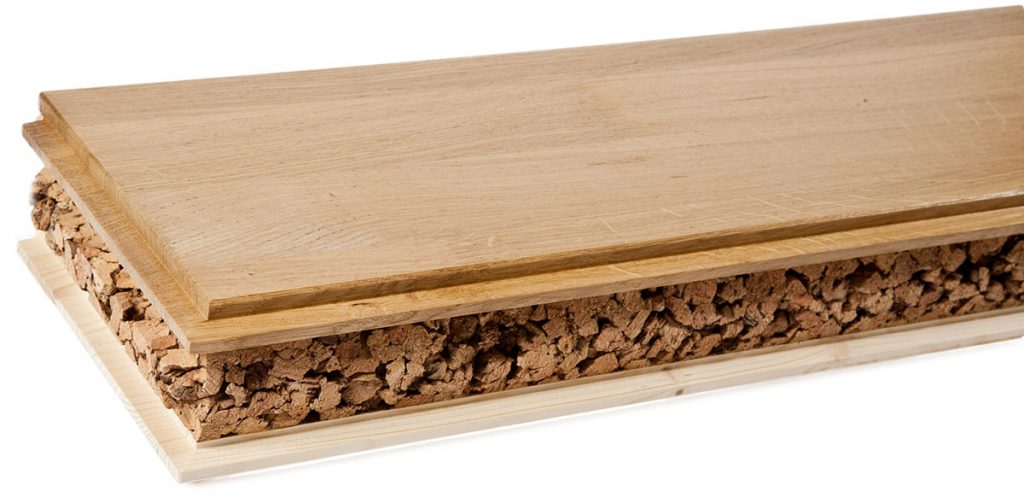
According to the Portuguese standards NP-114 and NP-273, cork powder is a material with dimensions smaller than 0.25 mm (Gil, 1997). There are different types of cork powder depending on the origin: grinding, granulating or pre-grinding powder; cleaning powder, no pollution; finishing powder from cutting and grinding operations; finishing powder for agglomerated cork slabs; finishing powder of agglomerated cork and discs; insulating powder for cork slabs (Gil et al., 1986).

A mixture of these powders is considered “flaming powder” as it is used to feed boilers due to its high calorific value (Fernandes et al., 2010; Gil, 1997). Other applications include use as a filler, mixed with adhesives, to improve the quality of corks, production of linoleum, use in agglomerates, briquettes, agricultural substrates, chemical sources (extracts)
Being an environmentally friendly and cheap material, cork powder can also be used to produce activated carbons with high specific surface areas, comparable to commercially available activated carbon, or it can be used directly for the adsorption of pollutants as a biosorbent. It is also used commercially as an absorbent during oil spills